|
So you've just had a contractor install 173 Access Points! Congrats! But, they haven't taken note of which one is where, nor did you create a table to show them which specific unit belongs in which location. Bummer dude! The problem with not knowing where each AP is is that you can't make finer adjustments of the system and troubleshooting location specific issues can be a nightmare.
There's an app for this problem... Well, maybe an API... Aruba Access Points have a function where each Access Point can advertise it's hostname in the beacon. It's still a manual job to go around and find each one with a survey tool or something like Wi-Fi Explorer, but it makes it easier than searching BSSIDs! To enable this handy feature on an Instant AP (or cluster) you can use the Command Line Interface (CLI). Go to the specific WLAN context and use the "advertise-ap-name" command. config
If you're using Aruba Central then you can't adjust the AP config via CLI. So you can use the API! For this particular feature (as of the date this is published) there is no specifically targeted API. You can use the AP Configuration API called "Replace AP configuration". With this essentially you are replacing the entire CLI for the Group or Swarm within a group. You can retrieve the existing CLI using "Get AP configuration", make your adjustments to include "advertise-ap-name" in the appropriate locations (for one fo the SSID profiles in the configuration) and then push it back to the AP using "Replace AP configuration". The specific use of the API is outside of the context of this blog post! Now go find an installer who documents their work!
Comments
Windows Netsh Commands
To see the SSIDs near the client netsh wlan show networks netsh wlan show networks interface=<NIC> netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid >> c:\testfolder\wirelessclientdata.txt mode=bssid adds more details about each network Find an SSID with specific text in the name: netsh wlan show networks | find “Employee" or netsh wlan show networks | select-string <your-SSID-name> Show WLAN profiles configured in windows netsh wlan show profile Wireless LAN Driver Properties netsh wlan show driver
ArubaOS (AOS) is the wireless LAN operating system for Aruba Instant Access Points and Wireless Gateways / Controllers. In AOS 8 you can use the following commands on a Mobility Controller (or a managed device, managed by a Mobility Master) to help troubleshoot various problems you may face with Access Points or Wi-Fi stations/clients.
These commands will need to be used directly on the controller (not the Mobility Master). You can jump to the controller by using the command mdc from within the Mobility Master (MM) CLI. First jump to the controller node-level with cd </md/node-hierarchy-path> so you are operating within the context of a particular managed node (controller/gateway/managed device). I prefer and recommend using this method over opening a direct SSH session to the single controller.
Take a look at the ap-debug statistics for a particular Access Points (AP). Look for Heartbeats, Interface counters, ARP cache Interface info, AP uptime, Ethernet Duplex/Speed, LMS info.
Check for high number of reboots or bootstraps (when the GRE keep-alive is missed).
It might be worth checking the AP system Profile for the “Bootstrap Threshold”. The current default is 8. If it is not specified in the config then its 8.
If your clients experiences issues there are commands to target statistics and logs specific to a station.
Look for tx/rx frames and data (if its incrementing then that’s positive), dropped frames, success vs retry.
Within the AP you can look at radio stats also. Look for radio resets, tx power changes, channel changes, noise floor, data drops and CRC errors increasing…
ARM history for the AP:
Show clients associated to a particular AP:
Aruba Downloadable User Roles (DUR) uses HTTPS. When the DUR is being issued by Aruba ClearPass the switch must trust the HTTPS certificate that the ClearPass server uses. The Certificate Authority intermediate certificate must be loaded into the switch as a trusted authority certificate. The public HTTPS certificate is automatically downloaded to the switch when a radius-server host, with type ClearPass, is configured on the switch (e.g. radius-server host <ip-address> clearpass).
To enable useful debugging certificate issues the following commands will work on an ArubaOS Switch.
If the switch detects any issues with the HTTPS process during a radius request which results in a DUR a debug message should be logged to the session window. During the SSL session there may be a lot of messages (it is noisy). Use 'no debug security ssl' to disable those messages.
When DUR works successfully the issued User Role will be specified in the Port Access Client Status output. To see information about the user-roles available and issued use the following show commands.
Ekahau has brought #WiFiDesignDay back to Australia for the second year running... It's great to have a local, low cost event to get Wi-Fi enthusiasts (users, managers, installers, sales people and manufacturers) in to the same room to celebrate and hopefully learn a thing or two about Wi-Fi. I'm writing (and updating) in real-time, so come back and refresh regularly for new content.....
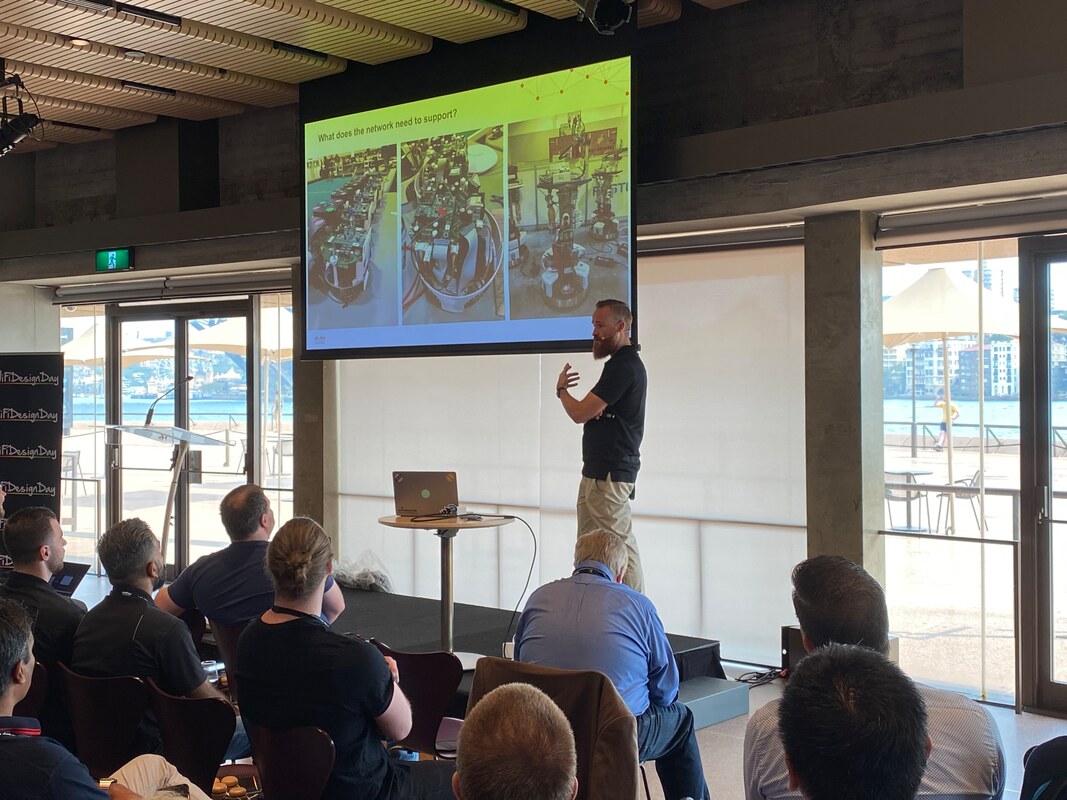
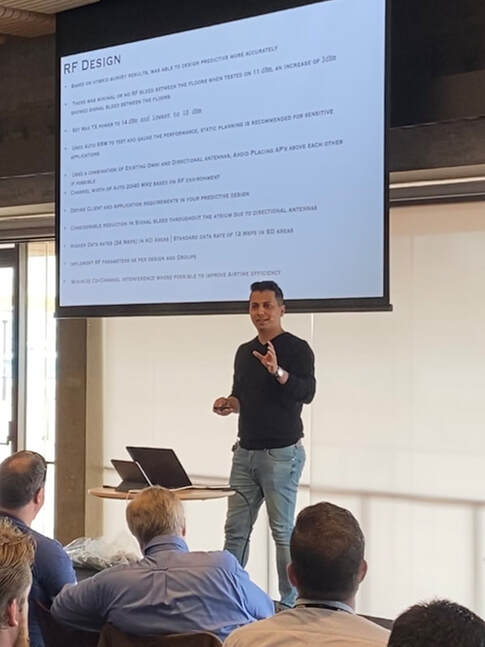
Kicking of the day was Antony Prasad and Amin Kroll (Ekahau) with some and awkward sales jokes but it led things well in to a quick demonstration from Grant Shelley (Ekahau) with iPhone in hand and Sidekick on hip surveying the conference space with the new auto-pilot feature that uses the internal phone gyro and camera-AR capability to automatically plot Grant's survey path on the map. This innovation is a brilliant step forward and well worth a test to see if it fits in your survey methodology! Mark Krischer (Cisco) - quickly handed the microphone to introduce Jonathan B from a local partner (Local Measure) based in Sydney to the stage to present quickly. Jonathan is the CEO and mentioned his company worked on the installation of Wi-Fi at the Sydney Opera House. He promoted his captive portal solution that helps "you extract more value" out of Wi-Fi, driving better user experiences with ability to opt-in to sharing information back to a venue. The portal allows for social login as well as other methods. The value to a venue is the ability to learn as much about a customer as possible while driving some operational efficiency with built in feedback forms. Back with Mark K for his topic of Understanding Wireless Security and WPA3. "A well designed wireless network will be more secure than the wired network that it connects to." Most wired networks do not use 802.1X for authentication. Mark takes us on a history trip on wireless security beginning with Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and why wireless security is important in the first place (no traditional physical security boundaries - like on a wired network). Mark explains that the Wi-Fi 6 certification is linked to the WPA3 certification - which means that inherently moving forwards we will have more secure networks. TKIP, SHA1 and WEP are now fully deprecated and Mark verbally recommends that instead of using these legacy measures to just leave the wireless network open. Importantly, Mark explains how MSCHAP is kind of broken now (it uses 3DES) which is commonly used with WPA-Enterprise and introduced Secure Fast Roaming which takes advantage of the IEEE standards 802.11k/v/r and Wi-Fi Agile Multiband. Management Frame Protection that "is going to immunise wireless networks from the vast majority of attacks we see today" (amongst the other newly introduced security measures). Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) will allow us to privatise data on an Open network using a invisible-to-user Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Rogue AP containment is a denial-of-service attack on another AP.  Darko Raic (Dicker Data) got up during the speaker transition to give away vouchers for the ESCE Troubleshoot class that is coming to Australia in the first half of 2020. If you're at the event, tweet and post to LinkedIn - this is the way to get a chance to win! I personally had the pleasure of attending a Dicker Data organised ECSE Advanced course this week (prior to #WiFiDesignDay) and Darko was very important to keeping each day run as smoothly as possible - I don't think I've been to a training as well run. Most importantly he had coffee delivery each day that you could have set an atomic clock to. Aaron Scott (Aruba) - Preparation!!! Earlier in 2019 Aaron managed the Wi-Fi for a pretty unique event that has requirements that fly in the opposite direction to some best practices. The lessons he learnt are valuable for us all. The Venue - every venue is different so setups between events will be different. You need to visit the venue in advance. Seeing the space is critical but you also need to check out cabling access/locations (IDFs and MDFs). An often overlooked part is the available Internet speed/bandwidth. Of course being able to get your eyes over the possible AP mounting/locations is super important - because you may be using "cable ties and duct tape" to get things in place. Taking measurements of wall attenuation and floor scale is smart. Meeting the venue team up front is also useful as you need them during the event and will most likely have to call in a lot of favours. Requirements - Least capable most important devices (LCMI) is what your network needs to be designed to support. This might be barcode scanners at an entry point or mobile devices, possible. But in the case of the event that Aaron had to support earlier in 2019 the most important devices were robots that were to play competitive soccer against each other. The Wi-Fi capabilities of these robots was wildly variant - some with antennas encased in a metal box, others with consumer grade wireless routers. For a robot playing soccer, having a low network latency is critical. RF requirements - stationary (keynote, breakout and meals). High roaming (walkways). Mixed (show floor). SSIDs for events typically are Open or Pre-shared Key (PSK) based. Most events don't use 802.1X authentication and these robots certainly didn't support 802.1X. At robo-cup there were approximately 46 SSIDs (not all broadcast out of all APs). Each field had it's own unique SSID and so there was no additional overhead introduced as each AP had a minimal number of broadcast networks. It is typically not a good idea to let devices talk to each other on the event wireless. Wireless to Wired communication was important so that robots could communicate with equipment on the side of the field. Pre-event negotiation on channel usage is a good idea. Often an event venue will want to broadcast there own public space SSIDs no matter what event is taking place. Coordinating channel plans with the venue is possible as long as it's well planned and the importance communicated up front. There are always unforeseen changes - map and venue layout changes all the way up to the day of the event. Being agile is important. Having extra APs ready for these changes is useful but also being prepared for some rapid re-planning. Dom Fitzgibbon (Plexnet) - Design, Deploy, Test, Survey, Monitor, Troubleshoot Wireless Life-Cycle Dom takes us through the Plan, Design, Verify, Test and Monitor cycle of Wi-Fi from his vast experience throughout his day to day. What to test: * AP authentication (WPA/WPA2/WPA3/802.1X * Average and maximum client capcity loading * AP stability * AP interoperability with legacy 802.11 mode * Benchmark L2-L7 throughput, Rate vs Range * Features : Roaming, Band Steering, Multi-AP mesh * 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) network readiness * Wi-Fi Offload (AP/Hotspots to LTE/5G) There is a lot to testing Wi-Fi (it's not as easy or simple as what we often model). Is iPerf a useful tool? Dom states it's great for quick testing but not always reliable past the 350-500 Mbps mark. iPerf should not be relied on as a definitive test result. Don't forget that security testing is very important. Ensure that Guest users can't hope into the corporate side of the network through firewalls or hopping the DMZ. Monitoring - it's a good idea to have monitoring in place even if it's as simple as SNMP. There are loads of third party tools so that you can employ and vendors have their tools too. Make sure the data you get is relevant to your business / dev ops needs. Packet data is critical (packets don't lie) and will tell you when you have application issues or if there are TCP problems. Wireless LAN Controller / AP telemetry must be understood but this takes some practice. The "wireless medium is a black hole" and often you know there is a problem in the network but don't understand why. Narrowing the issue to a floor or a single AP is helpful in narrowing your realm of troubleshooting. Benchmarking is critical so you know what it was like before a change or migration. When you're troubleshooting it's super helpful to know what things were performing before you were alerted to an issue. Finally - understand the ecosystem. DNS, DHCP, Authentication and Backhaul. It's very common that issues attributed to bad Wi-Fi are not actually Wi-Fi issues at all. Knowing how the whole solution ties together and the processes of how a client gets on the network will help you identify what is the root cause of a problem. Dom doesn't like buzz words and suggests we be aware of marketing hype! AI, Root Cause, Single Pane of Glass* AI = we aren't there yet... its machine learning and it's historical data analysis Root Cause = The system will help point you in the direction but it won't show you the answer, there is no magic bullet otherwise "someone would have come out with it" Single Pane of Glass = If you got everything in one view the screen would need to be massive and it would be painful to actually use. Useful tools * Wi-Fi Explorer Pro and Wi-Fi Signal by Adrian Granados https://www.adriangranados.com * WinFi Lite (Windows) https://www.helge-keck.com/download.html * WLAN Pi - does iPerf, Kismet & Speedtests. Great for ekahau throughput tests. https://www.wlanpi.com Keith Parsons (WLAN Pros) - Tips, Techniques and Tools for Troubleshooting Wireless LANs Check out his slides here: https://wlanpros.com/troubleshooting Occam's Razor "More things should not be used than necessary" - we actually have to take a complex route in Wi-Fi when troubleshooting. This is because Wi-Fi is easy to do wrong/badly... There are many examples Keith can give of complex systems (Fighter plans and historical airforce bombers, surgery etc.) and he suggests to overcome the problems caused by complexity we need a checklist. For an end-user "what are the things that could go wrong". Keith shows a snippet of the 400 items they documented when figuring out what happens on wireless, LAN or WAN that might cause "Wi-Fi" problems. After installing Cat6 cabling you verify and test it... you will get 1 Gigabit Ethernet every time on a successfully tested cable run. On Wi-Fi we need to test and verify that the Wi-Fi works to the requirements. One critical difficulty is that the requirements vary on every deployment and the customer often finds it hard to articulate those requirements. Knowing the requirements helps you fix issues - primary RSSI, secondary RSSI, acceptable level of Co-channel interference, when clients roam. You can only design for one client requirement so picking the right one is very important.  Attendees watching Keith Parsons at #WiFiDesignDay Attendees watching Keith Parsons at #WiFiDesignDay By surveying Keith knows that the PHY layer requirements are met or not (signal, interference, noise floors etc). Some people might start troubleshooting with a packet capture and make a decision from there. Keith suggests there is no one correct flow for beginning troubleshooting... The tool you start with may not give you the answers you need so you need to be well versed in all the tools so you can jump between them as required. Wi-Fi is an inefficient use of spectrum (vs LTE and other cellular based network technologies). Wi-Fi clients know nothing about the other devices ("all I know is about myself") and therefore the trigger for a client to know it is allowed to start transmitting is detecting "NOTHING" - Keith describes the 802.11 Contention Process. Density of Wi-Fi has nothing to do with number of APs - more so, density is reliant on clients talking fast. Talking fast means clients will have high signal, with good SNR which means a good data rate = fast transmittion of data. Fast transmission of data means that there is more airtime available for other clients to transmit = higher density. If you get the captive portal page, or if you got an IP address, or if your client can resolve a DNS address then Wi-Fi is not broken... These all require that data must travel across the Wi-Fi network to operate correctly. Keith skipped over the Captive Portal segment of his slides but the slides will be available soon so you can check out his views on that. Channels - use as wide a channels as you can until you cannot. Don't use wide channels when it is going to cause co-channel interference. 20 MHz wide channels is OK, but if you can get away with using wider channels then do. Don't be afraid of using DFS channels. DFS is only a problem when it is and the Wi-Fi network will alert you to this via logs. Keith breaks down the single frame transmission process. There is a lot of overhead and it's described well by a great / complex visual. I highly recommend CWNA and CWAP study to get to understand this process well. The spreadsheet for the single frame transmission is available in the Aruba Airheads community (most likely part of the Very High Density Validated Reference Design Guide by Chuck). Then Keith returns to Captive Portals, declaring them as evil. Disney World and the Apple Store don't have them so the excuse that it's a legal requirement is a bad excuse. To improve the performance of Wi-Fi (like on a wired connection) you must lower interference. This is how CAT Ethernet cabling has improved throughout the years - by twisting pairs or shielding and other techniques. The most prevalent cause of wireless slowness is other wireless. Lowering interference is a critical part of the deployment and troubleshooting process. Wired or Wireless Problem? * Ping is not a good troubleshooting tool - it's a layer 3 tool when you might have a layer 2 problem. * Does the client have an IP * Check the MCS of a Wi-Fi Client - * Is the issue isolated to Wi-Fi devices only? * Compare throughputs on Wi-Fi or wired connections * Check RSSI and SNR - the basic variable metrics for successful Wi-Fi PHY Keith shows an example of a great Wi-Fi client metric for a connection he had at a hotel in Dubai. The client had 867 Mbps data rate and -49 dBm with a -90 dBm noise floor (41 SNR) but the speedtest showed a 1Mbps download. This indicates either a rate shape somewhere other than the Wi-Fi or a terrible backhaul - in this case he spoke with the hotel and identified they were proud of their E1 connection to the Internet. Health Analogy: * Blood Pressures - Channel Utilisation * Pulse - Retry Rates * Temperature - MCS Rates Because clients back off and lower the MCS rates due to poor retry rates Keith focuses most on the MCS Rates rather than retry rates. This is great piece of advice for packet analaysis. Take the WLAN Pros Compensation Survey if you haven't already: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/WLAN_Comp_2020 Devaiah Nellamakada - Designing Wi-Fi in Multi-floor Buildings with Atriums Down the middle of the large building Devaiah designed for is a large Atrium with many floors of void space. Because of this there is plenty of RF bleed between floors, high SNR and CCI that must be managed as best as possible. It can make or break your user experience in those areas. Architecture is outside of the control of an RF Engineer. Open and high ceilings creates RF Reflection, multipath and unreliable signal quality. Multi-tenancy buildings have many challenges. AP channel planning is difficult and RF coordination may be impossible. Differing materials means large variance in attenuation. Factors than effect user experience * Lower throughput and disconnections * Unreliable Signal coverage and low SNR * Client devices and its NIC * Co-channel interference | ACI | low data rate * Non Wi-Fi Interference * Upstream Infrastructure Layer (L3-L7) * Multi-path fading, re-transmissions and reflection Discovery Approach
Monitoring is important for the team managing Wi-Fi long term. RF is invisible and the right tools will give you visibility in to what is happening. Key Design Factors
Not all clients are connected in an office at the same time, Consider over-subscription ratio 60-65% so that you don't end up with too many APs in the design. Design with client offset in mind - weakest client. , After Lunch Haydn Andrews (NTT) comes to the stage for Warehouse Wireless Design. Haydn kicks of with a hilariously painful video you may have seen online where a forklift driver taps a rack and the entire warehouse falls down around him. There are different types of warehouses you may come across... Safety:
RF Challenges
Warehouses are like snowflakes, each one is unique in it's own way. Never design a Warehouse without going on site at least once. Client Devices
Overhead omnidirectional antennas are easy to install and have large coverage areas so may mean less APs are required overall... but they are very susceptible to problems when stock levels change. They have issues with poor signal penetration and generally have a very large coverage area. Channel planning and co-channel interference can be a major problem when designing and configuring omnidirectional antenna APs. Directional antennas can potentially become obstructions to moving plant around the warehouse such as forklifts or trucks. They will generally have a good line of sight down a rack row and will ultimately provide higher signal to the clients. Typically directional antenna designs have more APs. SNR will improve and there is less chance of obstruction with well placed directional antennas. Warehouses are like snowflakes... Other considerations for APs: AP Enclosures are required particularly in places where AP is exposed to high dust, water or the outdoor elements. Low operating temperatures can be an issue in cold storage facilities - ensure that the AP model is capable of operating in the conditions of where you are mounting. Sometimes you can mount an AP outside the cold storage room and install antennas inside the harsh environment. Predictive Survey
AP on a Stick
Different Areas of a Warehouse to consider
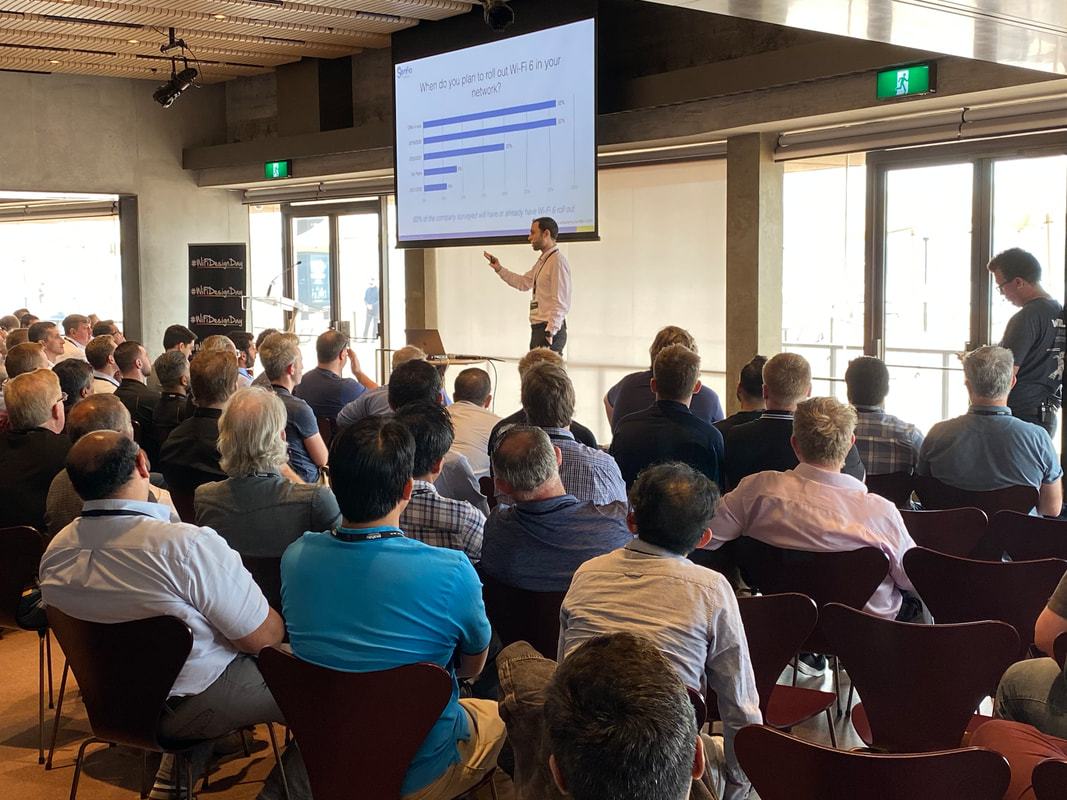
Some devices do not support DFS channels so be sure to design to the capabilities of the devices specific to the areas they are used. Knowing how the clients roam also helps the RF design. New types of client devices seen in this industry: IoT, Robots, Drones, Automatic Guided Vehicles Troubleshooting examples in a warehouse environment Common issues are coverage holes from old legacy designs. Often the layout of a warehouse has changed or where stock is stored has adapted which means the attentuation of stock has achanged the RF propagation. Roaming issues arise where large cells exist. Physical AP or antenna issues can arise and be difficult to diagnose. Rodents chew cables and of course upstream non Wi-Fi infrastructure related issues that get correlated to Wi-Fi problems by un-knowing users. The final presentation of the day is commencing with a tag team effort from Stephen Cooper (Mist) and François Vergès (Semfio Networks) who will talk about Design Considerations in Wi-Fi 6. 802.11ax or Wi-Fi 6 can be used interchangeably. Wi-Fi 6 is the Wi-Fi Alliances certfiication name based on IEEE 802.11ax technology. Wi-Fi 6 is going to be much more efficient than Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or the standards before it. It will use both the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands which brings new benefits to the 2.4 GHz space. MU-MIMO is no longer optional as it was in 802.11ac. To boil it down the advancements in Wi-Fi before Wi-Fi 6 were about making things faster but now we are improving the efficiency of clients on the area. There should be a lot less contention on the air thanks to Wi-Fi 6. Medium contention is improved with OFDMA. Most traffic over the air is about 300 bytes or less. So a lot of airtime was reserved for wasteful traffic. OFDMA provides much more efficient airtime/medium use by cramming what would have been multiple transmissions in to a single airtime use opportunity. Stephen is getting pretty deep in to the OFDMA Operations... his slides will be shared post-event so they will be better than a ton of bullet-points here. He is showing Trigger frame and RU allocation information within a wireless frame capture from Wireshark. We have finally reached full Wi-Fi Nerd level at #WiFiDesignDay. Stephen is using very clever analogies for the explanation of OFDMA and MU-MIMO - I can see a video camera in the back of the room so hopefully you can watch a video of his presentation at some point. With OFDMA there is a lot of negotatiation between clients and APs and it is fully dynamic. Devices can out-out of MU with resource units that are allocated for single device up-link transmissions. 1024QAM (modulation scheme) was introduced in Wi-Fi 6 which brings new data-rates. Not just fast data rates but slower data rates are now possible than before. Longer guard intervals are provided for more resiliency to provide a better chance of actually achieving 1024QAM. BSS Colouring provides greater spatial re-use which benefits times when there is channel overlap. Clients will maintain a 2nd NAV timer and there will be thresholds for the different BSS's. This is about improving channel re-use in highly contested environments. BSS = Basic Service Set OBSS = Overlapping BSS Target Wake Time (TWT) was first introduced in 802.11ah. Radio wake-up is no longer tied to the beacon/DTIM interval. It will make clients much more power efficient. It is feasible that a client may power it's radio down for very long periods (days maybe). Wi-Fi 6 can be detected by Wi-Fi Explorer Pro, Ekahau Sidekick, Packet captures, your device if it supports Wi-Fi 6. Handing over to François... who made a cheeky comment on the number of new acronyms introduced by Wi-Fi 6. François is on his first trip to Australia and has been taking the ESCE Advanced course in Melbourne this week prior to #WiFiDesignDay. The design requirements for a Wi-Fi 6 design may have some changes around the models of clients and APs. AP models that support Wi-Fi 6 may have higher power requirements. François showed some examples of power requirements from Cisco, Ruckus, Mist and Aruba. We need more power because we might support up to 8 spatial streams - 8x8:x APs are coming in the near future. They will most likely require 802.3bt (51-71W) or dual 8023at (2x 25.5W). The new higher power PoE standards will require new switches. Wi-Fi 6 Clients on the market are Samsung Galaxy S10, iPhone 11 and the Intel AX200/201 chips for laptop devices. The spatial stream capabilities on these devices are similar to what we are seeing in todays 802.11ac devices (such as 2x2). We may see a new subset of client device types with the introduction of Wi-Fi 6 - IoT will change the network requirements because of the need for Target Wake Time, MU-OFDMA and specifically to support the 2.4 GHz 802.11ax implementation. The same amount of spectrum is available to date. So channel planning will be much the same as with 802.11ac. Not much should change here. We will use the spectrum we have in a more efficient way - which may effect capacity planning. Most likely we will still use 20 and 40 MHz wide channels. Wi-Fi Agile Multiband is a pre-requisite for Wi-Fi 6. Neighbour reports, BSS Transition features and Over-the-air Fast Transition are new capabilities enforced. The clients will be smarter and we should see better roaming. We currently try to calculate the amount available airtime on a serial transmission basis based on the number and types of clients on the network. This will change because of new dimensions of Wi-Fi 6. The capacity is effected by MU-OFDMA, MU-MIMO, TWT, BSS colouring and 1024 QAM. It's unknown at this time how the vendors will allocate things like Resource Units so it will be difficult to do maths on capacity until more is known about the implementations. If the information is not available we may have to make some educated guesses. Some Wi-Fi 6 features might not be supported or enabled all of the time. There are likely to be a lot of moving pieces which adds to the complexity of how a wireless network is operating. Design Tools!!! We need new capabilities
Ekahau will still be a major part in the design and management life-cycle of wireless networks.  Stephen and François doing the full on-stage nerd-out with Wireshark @ #WiFiDesignDay Stephen and François doing the full on-stage nerd-out with Wireshark @ #WiFiDesignDay Stephen and François are game enough to try a live packet capture with Wi-Fi 6 capable devices connecting to a Mist AP. They attempted to show how OFDMA will slice up the channel for multiple simultaneous client transmission. We could see some hints of it on the screen which was pretty cool. Next was a packet capture to identify the presence of OFDMA. It was easy to follow along with the stream in Wireshark because of the clear frame colouring that François had installed in his Wireshark. That's a Wrap! What a wonderful day... another #WiFiDesignDay done in Australia. |
WifiHaxWe build and optimise networks. Continuous learning is our secret to being good. Along the learning journey we will share things here... Archives
November 2022
Categories
All
|








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed